Abstract
Background:
The standard of care for younger patients with mantle cell lymphoma is induction chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Rituximab (R) maintenance therapy post induction has been shown to improve overall survival (OS) (Kluin-Nelemans et al. NEJM 2012), and R maintenance post ASCT has been shown to improve progression free survival (PFS) (Graf SA et al. Ann Oncol 2015) and OS (Le Gouill S et al. ASH 2016). Bortezomib as consolidation has been shown to be feasible and tolerable in patients with MCL post ASCT (Kaplan L et al, ASH 2015). We hypothesize that the combination of bortezomib plus R as maintenance therapy post ASCT in patients with MCL may increase the disease free survival (DFS). We report our final results including quantitative CCND1 mRNA monitoring for minimal residual disease.
Methods:
This is a multicenter phase II maintenance study in patients with MCL post ASCT. Bortezomib was given at 1.3 mg/m2SQ once a week for 4 weeks every 3 month for 2 years. Rwas given at 375 mg/m2 IV once a week for 4 weeks every 6 months for 2 years. CT and/or FDG-PETwere performed at every 6 months. The primary endpoint was to reach a 2 year DFS of > 80%. Secondary endpoints included toxicity, relapse rate, OS, and CCND1 mRNA as MRD monitoring. Peripheral Blood was collected at baselineand on day 1 of each cycle (3 month interval), and CCND1 mRNA was assessed using droplet digital PCR technology (ddPCR) on RNA extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. JVM2 (MCL cell line), normal healthy patient, and an untreated patient with MCL involvement served as controls. Absolute transcript concentrations were normalized to HPRT1 (housekeeping gene) followed by a normalization to the positive control, JVM2 (100%).
Results:
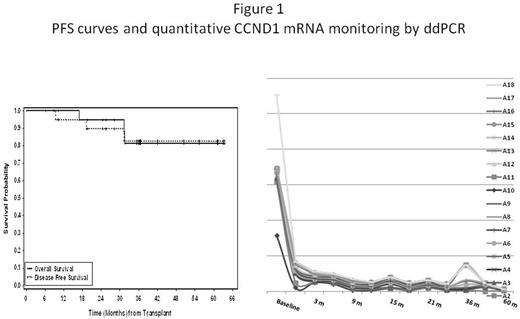
Twenty three patients were accrued, with 23 eligible for analysis. Majority of the patients were male (96%), received ASCT and maintenance therapy in CR1/PR1 (91%), had advanced stage at diagnosis (70% stage IV), and considered young with a median age of 59 (45-66). About half had low risk disease by MIPI and half with intermediate to high risk disease. The median follow- up was 29.8 months. The 2 year DFS is 89.7% (95% CI: 64.8-97.3) and 2 year OS is 94.7% (95% CI: 68.1-99.2) for the whole cohort (Figure 1). The 2 year DFS is 94.4% (95% CI: 66.6-99.2) and 2 year OS is 100% (95% CI: NA) for the 21 patients who received induction therapy followed by ASCT and R maintenance in CR1/PR1. Two patients who entered trial had relapsed/refractory MCL.
Treatment was well tolerated. The median number of completed cycle was 8/8 (1-8) with a median duration of therapy of 19.9 month. Grade 3/4 toxicities possiblyattributable to study drug included neutropenia (n=17), lymphopenia (8), pneumonia (2), anemia (2), skin infection (1), hyperglycemia (1), and thrombocytopenia (1). Grade 2 possibly related toxicities that occurred in > 10% included upper respiratory tract infection (5), hypertension (5), diarrhea (3), fatigue (3), neutropenia (1), and thrombocytopenia (3). With regard to the specific adverse event of peripheral sensory neuropathy, Grade 1 event occurred in 10 patients and Grade 2 in 2 patients. There were no treatment discontinuations due to neutropenia or neuropathy. There were 2 death on study, 1 from relapsed MCL and 1 from alloHCT for MDS.
MRD monitoring was performed on 18 patients seen at COH. Twelve out of 18 patients had at least 36 months analysis while 6/18 had less than 12 months for analysis. High CCND1 mRNA was detected in an untreated patient (control) with MCL involvement and JVM2 cell line. Low CCND1 mRNA was detected in normal healthy control, all samples while on maintenance R, and all patients without radiographic progression of disease (Figure 1). . Unfortunately, no samples were obtained on the two patients who developed progressive disease (1 due to withdraw of consent prior to relapse, the other due to urgency of treatment).
Conclusions: The combination of bortezomib with R as maintenance therapy for MCL is well tolerated post ASCT and has met the primary endpoint of prolonging 2 year DFS. Quantitative CCND1 mRNA monitoring by ddPCR is feasible and appears to correlate with clinical remission status. The combination therapy of bortezoimb and R maintenance therapy post ASCT and CCND1 mRNA MRD monitoring method warrants further investigations.
Chen: Pfizer: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Speakers Bureau; Affimed: Research Funding. Nademanee: seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau. Siddiqi: Juno: Other: Steering committee for JCAR017; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie Company: Other: Steering committee for ibrutinib, Speakers Bureau. Kwak: Pepromene Bio: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Celltrion, Inc: Consultancy; InnoLifes: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Holmberg: Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; JAZZ: Consultancy; Up To Date: Patents & Royalties.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal